- The importance of digitisation and personalisation
- It’s all about the data
- The role of artificial intelligence and machine learning
- How blockchain helps shape the future of banking
- Fintechs, digital-only banks, challenger banks, and neobanks
- New players transforming the banking game
Like many other sectors, the financial services industry is also increasingly feeling the pressure to embrace emerging technologies, become more and more digitalised, and adopt new business models. And while AI and automation have already proven to be of great value in the banking sector, and cloud computing and blockchain technology are leading to innovations across the industry, challenger banks and financial technology companies are appearing left, right, and centre, and customers are increasingly managing their personal finances from their smartphones. And with customer expectations being very different from what they were only a few years ago we will see even more rapid innovation, not necessarily from within the banking industry, but increasingly from startups that are looking to take a huge part of the market. And they will do this by providing more than just financial services and improving mobile and online offerings.
Personalised services are among the most important factors for customers to have trust in their banks. But only a third of traditional banks offer the kind of personalisation that actually meets their clients’ needs.
The importance of digitisation and personalisation
For traditional banks who want to diversify and personalise the services offered to their customers, digitisation is critical. This entails a transition to offering online and digital services, as well as the implementation of artificial intelligence, blockchain technology, and data analytics. Many already invest significant capital in digitisation in order to improve the customer experience, automate processes to streamline service delivery, free up staff for more valuable tasks like customer relationship building, and improve online security. Some benefits of digitalisation in banking include more efficient processes, which in turn translates to improved value and a better customer experience. The increasing digitisation will also lead to more transparency, enabling customers to easily compare services and products in real-time. Banks will also be better able to meet the needs of their customers by personalising their experiences based on the data they collect. This results in improved customer loyalty and retention. Offering digital services also leads to more detailed insights, which translates to improved decision making and fewer operational errors and costs.

More than 50 per cent of bank customers say personalised services are among the most important factors for them to have trust in their banks. But only a third of traditional banks offer the kind of personalisation that actually meets their clients’ needs. This means that, in order to retain their loyalty and trust, banks will have to invest more than ever to personalise their service offerings. And according to EPAM Continuum’s 2021 Consumer Banking Report, which surveyed 21,000 banking customers across The UK, Canada, the US, Germany, The Netherlands, Hong Kong, and Singapore, 34 per cent of respondents want more personal interaction with their banks via actual interactions with human support agents.
It’s all about the data
And the more digital services a bank offers, the more data they will have, and the better they can identify opportunities and optimise and personalise their products and services. Data is often referred to as ‘the new oil’, due to its ability to enable collaboration and personalisation in this brave new world of banking. Essentially, the bank of the future will be a data company, leveraging technology, aggregating value, providing advice, and facilitating access to an increasing array of services and products. The foundation of the bank of the future comprises a connected and comprehensive view of all data. And automating back-end processes, creating seamless connected experiences, understanding fast changing customer behaviours, and optimising compliance and risk requirements all demand a solid data platform.
Digital identification profiles will enable customers to increasingly take control of their own data, with banks becoming ‘trust brokers’, if you will, in terms of the safeguarding and management of these digital IDs and brokering access to 3rd-party services – such as retailers and utilities – outside financial services. And according to studies by Capgemini and Boston Consulting Group, 80 per cent of people trust banks to manage their data, which means that banks are already in a strong position to take on the enhanced role of data managers. In the near future, as a result of these developments, banking will become increasingly seamless, with services such as investments, loans, and savings all optimised based on the customer’s data profile.
“Some 86 per cent of financial services AI adopters say that AI will be very or critically important to their business’s success in the next two years.”
Source: Deloitte
The role of artificial intelligence and machine learning
In the years ahead, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics will become increasingly important and permeate even more aspects of banking. The technologies are already used in customer identity validation and authentication and advanced fraud detection. Artificial intelligence and machine learning enable superior understanding of customer preferences and help banks to deliver personalisation at scale to create vastly improved customer experiences, products and services.
Artificial intelligence can be used to develop personalised loan offerings based on information like shopping behaviour, credit history, and other data, enabling each customer access to a unique offering that’s specifically tailored to them. Another trend that’s already becoming apparent is AI-powered lending decisioning, as well as AI-powered retirement planning and portfolio management – which can help develop smart investment and retirement plans that are uniquely designed to a customer’s preferences and characteristics, such as personal goals and risk tolerance. These technologies will also enable banks to become digital value collectors and provide a digital archive for everything in the customer’s life, enhancing customer relationships and loyalty and improving profitability.
According to a recent Deloitte survey of IT and line-of-business executives, 86 per cent of financial services AI adopters say that AI will be very or critically important to their business’s success in the next two years.
How blockchain helps shape the future of banking
Blockchain is used for person-to-person transactions but as international payments via blockchain are much cheaper compared to traditional methods, it is also increasingly used by banks for international money transfers. International payments via blockchain also do not require a third-party authorisation, which makes it a much faster process than traditional money transfer methods. Blockchain also enables the centralisation of the online identity verification process, so that users only need to verify their identity once, after which they can share it with any service provider of their choosing. Blockchain can significantly simplify and speed up share trading as well. While traditional share trading can take approximately 3 days to complete, by eliminating all the intermediate steps and minimising the information redundancy in the system, share trading using blockchain can be done instantly.
Blockchain can also provide excellent ways to speed up and streamline the process of accessing credit reports from credit companies – which are used for approving or declining loan applications – and ensuring that these reports are accurate and transparent. Transaction tracking can also be significantly improved upon with blockchain technology by building an extremely secure decentralised transaction register which will virtually eliminate fraud and data redudancies. Once blockchain becomes a global standard, as it’s currently not yet widely adopted in the banking industry, it will enable faster transaction processing, improved transparency, and significant cost reductions.
The Kenya-based startup BitPesa applies its advanced technology to open new payment corridors between Africa and the world, to enable customers to send and receive near-instant and low-cost payments without having to use a bank account or digital wallet. With subsidiaries across the UK and Africa and licensing by the FCA, BitPesa was the first company in the region to make a market between traditional and digital currencies. BitPesa’s platform makes use of cutting-edge blockchain technology to enable companies to transfer money to suppliers, distributors, and employees, and receive payments from African customers in local currencies. The fast and efficient transactions rely on GBG’s identity verification services, a global specialist in Identity Data Intelligence. Using the company’s ID3global platform, BitPesa automates their customer sign-up process and runs money laundering checks, reducing delays and increasing BitPesa’s bottom line. Using GBG’s expertise in digital currencies and advanced global verification services, BitPesa is continuously growing its success with crypto-orientated services in Africa.
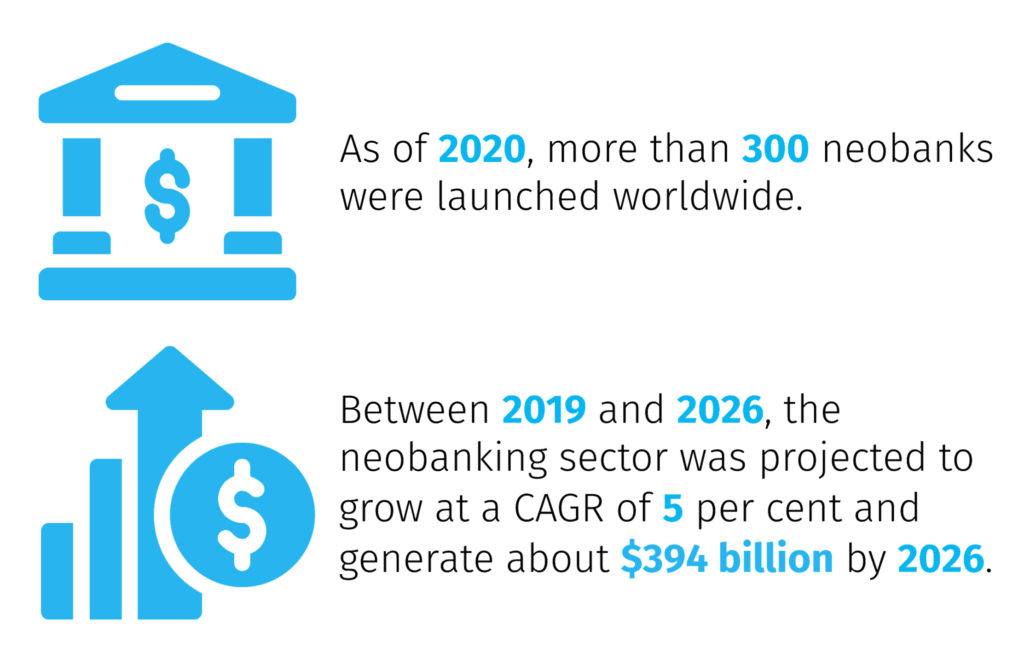
Fintechs, digital-only banks, challenger banks, and neobanks
Fintechs (financial tech startups), digital-only banks, and neobanks are all a type of challenger bank – new types of financial services providers that adopt a digital-first approach and focus on delivering excellent customer experience. As their name suggests, challenger banks literally challenge conventional banks by continuously innovating and rapidly expanding their client base. In fact, they are gaining more and more popularity every year. Although they typically don’t have or require physical presence, (and neobanks don’t need a typical banking licence), in most other cases, such as in terms of their services, they are similar to traditional banks. They offer convenient and user-friendly apps for banking services, such as almost real-time new account opening, instant activation of digital payment cards, options to instantly freeze a stolen or lost payment card via the app, immediate notifications when making a card payment, visual overviews of spending patterns, convenient budgetting and saving options, and more. And all of this without having to visit a physical bank branch – and generally without any of the usual hidden fees and hefty pricing policies of traditional banks. What’s more, challengers also cater for the unbanked, which is why they are so popular in all regions across the globe.

According to Zion Market Research forecasts, as of 2020, more than 300 neobanks were launched worldwide. Between 2019 and 2026, the neobanking sector was projected to grow at a CAGR of 5 per cent and generate about $394 billion by 2026. The success of these challenger banks has enabled companies from non-finance backgrounds to move into the market, with some experts believing that almost any enterprise with a certain amount of customer trust can theoretically become a bank. “The next bank does not have to start out as a bank. The next era of financial services will come from seemingly unexpected places,” writes Angela Strange for Andreessen Horowitz, a private American venture capital firm, founded in 2009 and headquartered in California.
New players transforming the banking game
While these new players in banking don’t – yet – have the customer base or the funds to eclipse traditional banks, they do offer something else that’s critical – innovative products and services. This means they can quickly form partnerships and launch new features in order to serve customers much more efficiently, cheaper, and faster than traditional banks can. They offer customers banking services directly on their mobile phones or via other digital platforms. The UK is currently leading the race when it comes to challenger banks and neobanks, but lots of other innovative, digital only banks have emerged in other parts of the world as well. As of April 2022, there are 249 neobanks worldwide. Here are some examples:
Hello bank!
Hello bank! is a digital direct bank owned by BNP Paribas. The bank supports its customers in taking their financial independence into their own hands and operates in France, Belgium, Austria, Italy, and the Czech Republic, as well as in Germany under the name Consorsbank. Towards the end of 2020, it processed more than 1.8 million securities transactions. Hello bank! claims to be the first fully digital mobile bank in Europe and offers its clients current and saving accounts, insurance, mortgages, loans, personal budgetting tools, debit cards and prepaid credit cards, and enables the management of all transactions from an iPhone or Android application.
Statrys
Statrys is a Hong Kong-based digital payment services platform that has been in operation since 2018. It specialises in virtual international business accounts, with all the features traditional banks offer, but without the hassle and the red tape. It provides SMEs around the world with payment and forex solutions and is known for its transparent, dependable, and affordable service. Positioned as a digital alternative to traditional banks, Statrys supports single-currency as well as multi-currency accounts, provides 24 hours human customer support, and offers payment cards as well as trade financing services. “We launched Statrys at a tipping point. Businesses had woken up to the fact that traditional banks do not have the tech, the efficient processes, nor the customer focus, to offer competitive payment solutions,” said Statrys founder and CEO Bertrand Theaud.
N26
This German neobank is headquartered in Berlin and provides services to some member states of the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) as well as to the United States. Since its launch in 2013, N26 has more than 7 million customers in 25 markets, where it offers services to private as well as business users. It offers free payments worldwide, no withdrawal or monthly fees, no credit card fees, free basic current account, 24-hours chatbot support, and provides debit Mastercards. Its features include push notifications for every transaction in your bank account, which helps keep an eye on spending and unexpected transactions. N26 also automatically enables customers to categorise transactions – you can easily search through them, and see statistics for each month. The N26 app and website are in English, as is their customer support. Besides German and English, the app is also available in Spanish, French, and Italian.
Monzo
The UK-based neobank Monzo was one of the first of a number of new challenger banks in the UK. It started out with offering a prepaid card, but transitioned to a full current account in 2018 and now works like many other accounts. You get a Mastercard debit card and you can download bank statements. Monzo holds a bank license in the UK and Australia and is currently expanding to the US. Monzo can be used all over the world where Mastercard is accepted and is famous for its budget planning features. The neobank launched a business bank account in March 2020 to enable it to provide its services to business users as well. Its features include free bank transfers within the UK, no monthly fees, no minimum balances, budget and spending categorisation, real-time push notifications, historical transactions, and 24/7 customer support. Customers can categorise their transactions, freeze lost or stolen cards, and view an overview of their spending habits.
Revolut
The UK-based neobank Revolut started out in 2015 with travel cards that provide cheap exchange rates. In the last six years, Revolut has gained more than 5 million customers and also obtained an EU banking licence. Revolut’s aim is to become the world’s first global bank, and has been expanding its services to various countries in Europe and the US and will soon launch in Hong Kong as well. Revolut offers its customers the option to buy and sell crypto currencies and stock, accepts 150 different currencies, doesn’t charge for exchanging standard currencies, and provides weekly spending insights.
Holvi
The Finnish digital all-in-one banking service Holvi is targeted at freelancers, the self-employed, and European micro-entrepreneurs. The firm also has offices in Madrid and Berlin, provides personal and business accounts, and helps users run their businesses by offering an intuitive, affordable, and user-friendly banking service. This includes expense mаnаgеmеnt tооls, streamlined invoicing, bookkeeping, expenses overviews, tax, and real-time business insights. Holvi serves entrepreneurs ranging from consultants and event organisers to bloggers, traders, and yoga instructors – and anything in between. Holvi’s customer support team provides great value through the support and services it offers and takes customers’ interests at heart. While established in Finland, Holvi’s company language is English and its website is available in English, German, and Suomi.
Chime
Chime is a US-based financial technology company that partners with Stride Bank and Bancorp Bank and is founded on the premise that basic banking services should be easy and free. It offers a platform that eliminates many of the fees usually associated with traditional banks and doesn’t rely on overdraft fees, monthly service fees, minimum balance requirements, and so on. Its features include automatic saving tools, early access to direct deposit payments, credit-building opportunities, credit and debit card services, no foreign transaction fees, and a competitive interest rate on savings accounts. Chime does not offer loans and financial products.
Bunq
The digital bank Bunq, whose founders are Dutch, launched in 2015. The bank enables its customers to access their accounts from all European countries. Transfers and payments without additional fees are the most appreciated features of the platform, particularly among travellers. Bunq’s Mastercard and Maestro cards enable customers to withdraw or spend money anywhere in the world without worrying about ATM access or currency exchange. Bunq is committed to a diverse, green, and inclusive future for everyone and claims to be the only bank in the world that enables its customers to choose how their money is invested. For every €100 spent with any of its cards, Bunq will plant a tree through its partnership with Eden Reforestation Projects.
In closing
The financial sector is undergoing a major digital transformation driven by the pandemic and changing consumer expectations. The growing transition to online and mobile devices is putting enormous pressure on financial institutions to offer increasingly personalised, digital-first services that enable access to fast, engaging, and interactive customer experiences. Not only do customers increasingly expect their banks to enable them to manage their money remotely, but they also want them to predict and meet their expectations almost instantly. From innovative payment methods to digital banks and AI financial advisors, technology is becoming an increasingly important asset in the banking sector, forever transforming the way we spend, borrow, budget, and save money. According to Ferenc Böle, head of IT Project Management and Transformation Directorate at OTP Bank, “Many banks are still at the beginning of this road to transformation. We have to be aware that there will be obstacles, and that there may be conflicts with existing projects that need to continue. Despite all of that we need to invest in technology today that will allow us to harvest benefits in the future.”




