- What exactly is a human digital twin?
- The rise of human digital twins in drug and vaccine development
- Human digital twins in education and training
- Create a virtual clone of yourself and live forever — digitally
- Beware the evil digital twin
The intriguing concept of digital twins is rapidly transforming fantasy into reality. These virtual replicas, once confined to industrial applications, are now being developed for the most complex systems we know: human beings. Imagine having a digital counterpart that not only looks like you but also behaves and responds as you would. It’s not just about creating a lifelike avatar; it’s about creating an entity that can track your health in real time, predict potential illnesses, and allow for the testing of treatments in a virtual space with no physical risk. Digital twins could personalise patient care, make drug trials safer, and bring new medications to market with unprecedented speed. But the scope of digital twins extends beyond the clinical. In education and training, for instance, digital twins could enable bespoke learning experiences. They could be our personalised tutors, tracking our knowledge and skills, and adapting our learning paths. And for those with an eye on eternity, creating a digital twin could be a step towards immortality, ensuring your thoughts, stories, and essence can be accessed for generations to come. In this article, we will explore the (potential) applications, benefits, and ethical considerations of human digital twins.
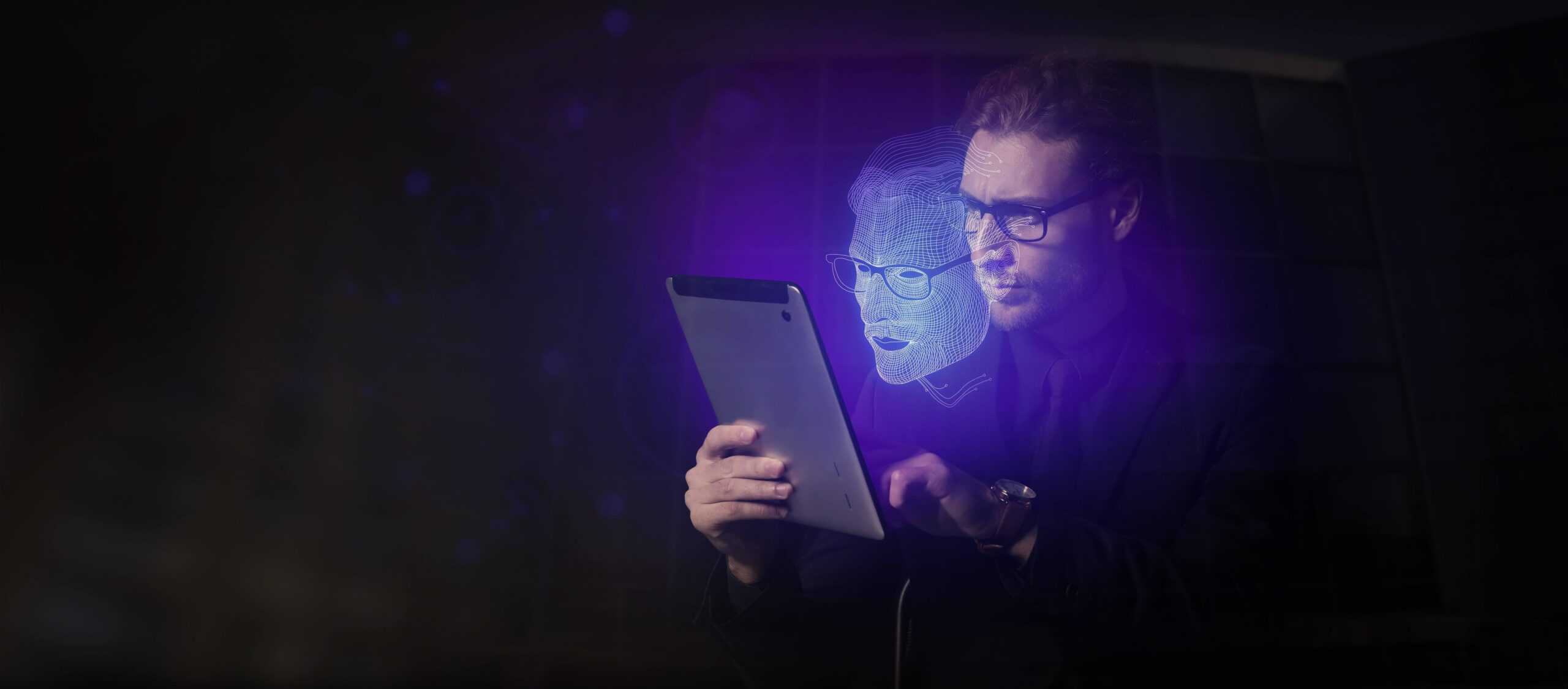
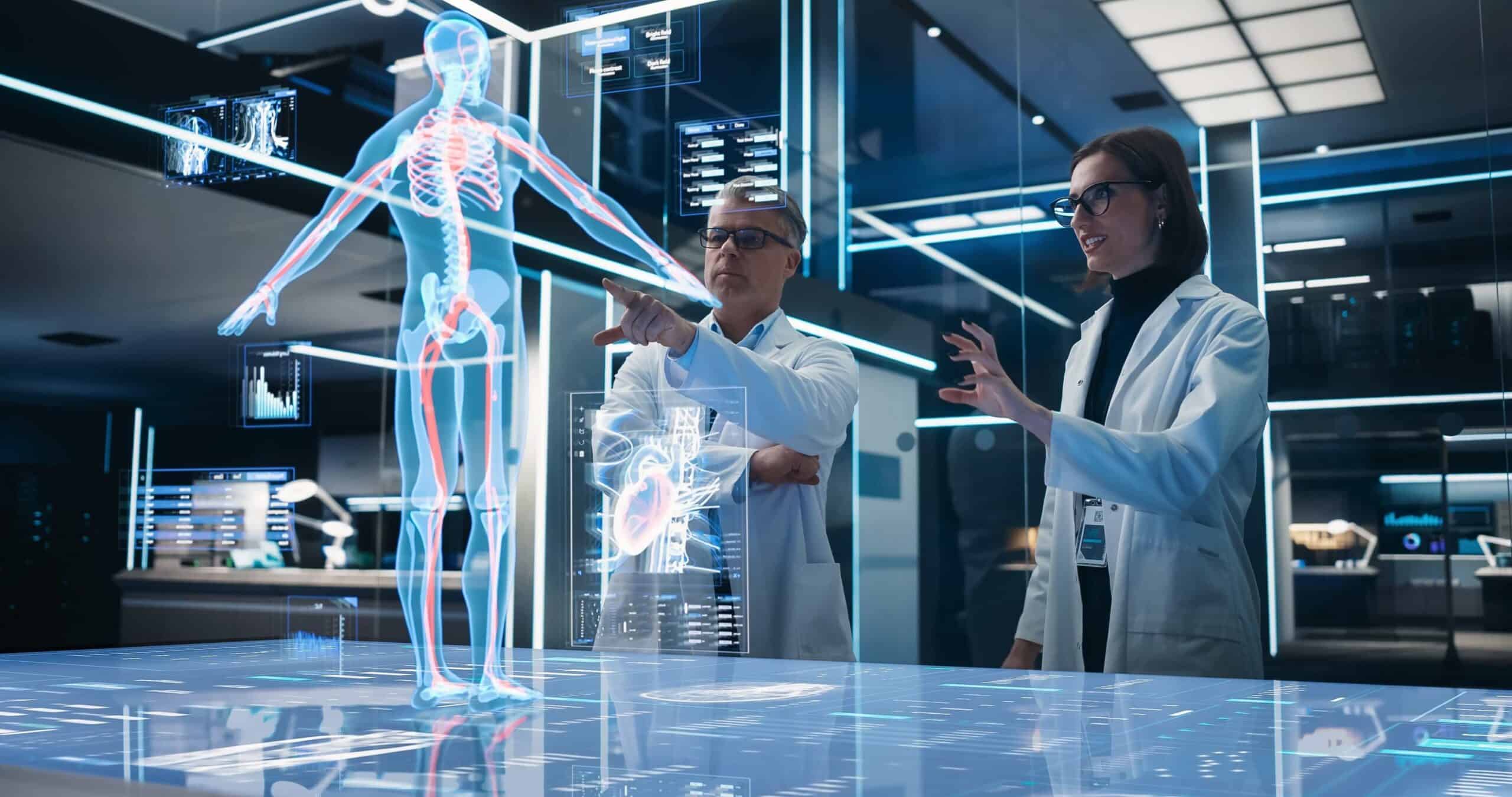
What exactly is a human digital twin?
A human digital twin is an advanced technological innovation designed to create a highly detailed digital representation of an individual, encompassing more than just physical appearance to include biological, behavioural, and environmental characteristics. This concept integrates sophisticated computing, data science, artificial intelligence (AI), and biometrics to craft a dynamic model that evolves in real time alongside its human counterpart. The technology behind human digital twins relies on continuous data collection through wearable devices and sensors, capturing vital health statistics, physical activity, personal preferences, and environmental interactions. This wealth of data serves as the foundation for the digital twin, which is constantly updated to accurately reflect the individual’s current state.
The role of AI, particularly machine learning, is central to the functioning of human digital twins. By analysing the collected data, AI algorithms can simulate our behaviour, predict future health outcomes, and adapt to changes, ensuring the digital twin remains a true reflection of ourselves. This process involves a sophisticated understanding of data patterns and the ability to refine predictions as new information becomes available, highlighting the dynamic and evolving nature of the digital twin.
The potential applications of human digital twins are vast and transformative, especially in areas like healthcare, education, training, and even digital ‘immortality.’ In healthcare, digital twins could completely change personalised medicine by offering tailored health assessments and treatment plans. They can also serve as personal agents or proxies in virtual environments, attending meetings, conducting negotiations, or performing tasks on behalf of their human counterparts, thus extending human capabilities into cyberspace. This capability also opens up opportunities for unique interactions, such as dialogues with past or future selves or even with historical figures, thereby enriching personal growth and decision-making processes.
The use of digital twins as interfaces in cyberspace can enhance or augment human abilities by merging or exchanging skills with digital counterparts, thus overcoming physical or cognitive limitations. However, realising digital twins’ full potential requires careful consideration of ethical, privacy, and security implications. This necessitates a multidisciplinary approach that includes experts from the social sciences, humanities, natural sciences, and technology sectors. As research and development in this field continues, the integration of various existing and emerging technologies will be crucial in shaping the future of human digital twins, offering unprecedented opportunities for personal and societal advancement.
The global digital twin market size was valued at $8.60 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow from $11.51 billion in 2023 to $137.67 billion by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 42,6 per cent during the forecast period.
Fortune Business Insights
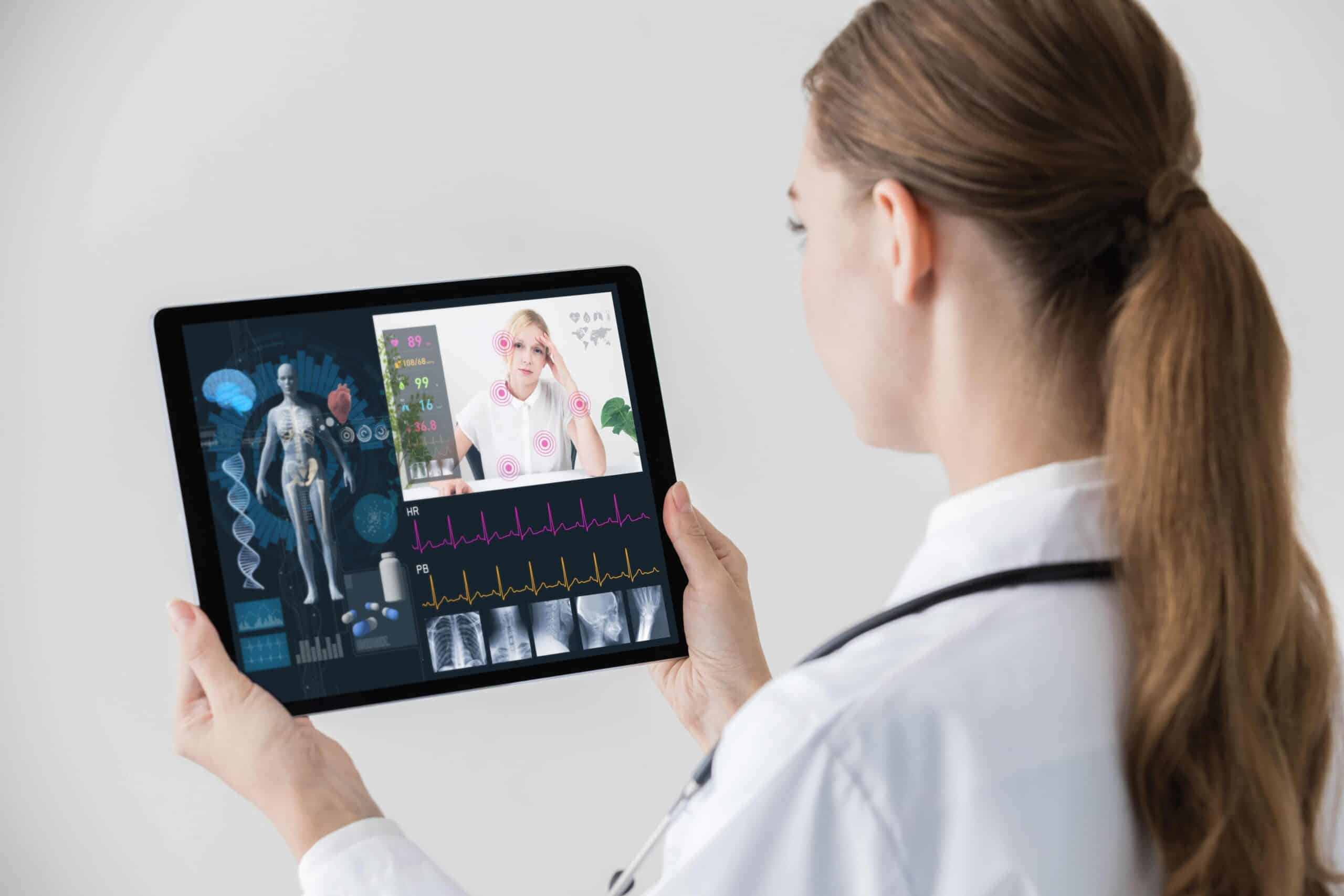
The rise of human digital twins in drug and vaccine development
Human digital twins are changing personalised medicine by using individual genetic, environmental, and lifestyle data to tailor treatments. This approach improves treatment efficacy and reduces side effects, marking a significant shift towards customisation in healthcare. Human digital twins — in healthcare also known as virtual patients — are integral to the research and development phases of medical treatments, especially within clinical trials. By simulating the human body’s response to new drugs or therapies, digital twins facilitate safer, more efficient testing, accelerating the development of effective medical interventions.
The concept of using human digital twins, or ‘in silico medicine’, offers a groundbreaking method for early-stage testing of drugs and vaccines. By creating virtual models of human organs or body systems, researchers can predict how actual humans might react to new medical interventions. This approach is particularly valuable in vaccine development, where virtual humans can be used in initial trial phases to screen out vaccines that are unlikely to be effective. This accelerates the research process by allowing for rapid, cost-effective preliminary assessments. It also enhances safety by reducing the need for human volunteers in the early testing stages. The technology behind virtual patients involves sophisticated imaging techniques that capture detailed anatomical data of an individual’s organs. This information is then integrated into complex mathematical models that simulate the physiological functions of these organs.
Advanced algorithms process this data, solving intricate equations to generate a digital counterpart that mimics the real organ’s behaviour and response to potential treatments. One of the practical applications of this technology is the HeartFlow Analysis, a non-invasive diagnostic tool approved by the FDA. It makes use of CT images to construct a dynamic model of blood flow through the heart’s coronary vessels, improving the diagnosis and treatment planning of coronary artery disease without the need for invasive angiography. By simulating how different treatments affect an individual’s virtual model, healthcare providers can tailor therapies more precisely, improving patient care.
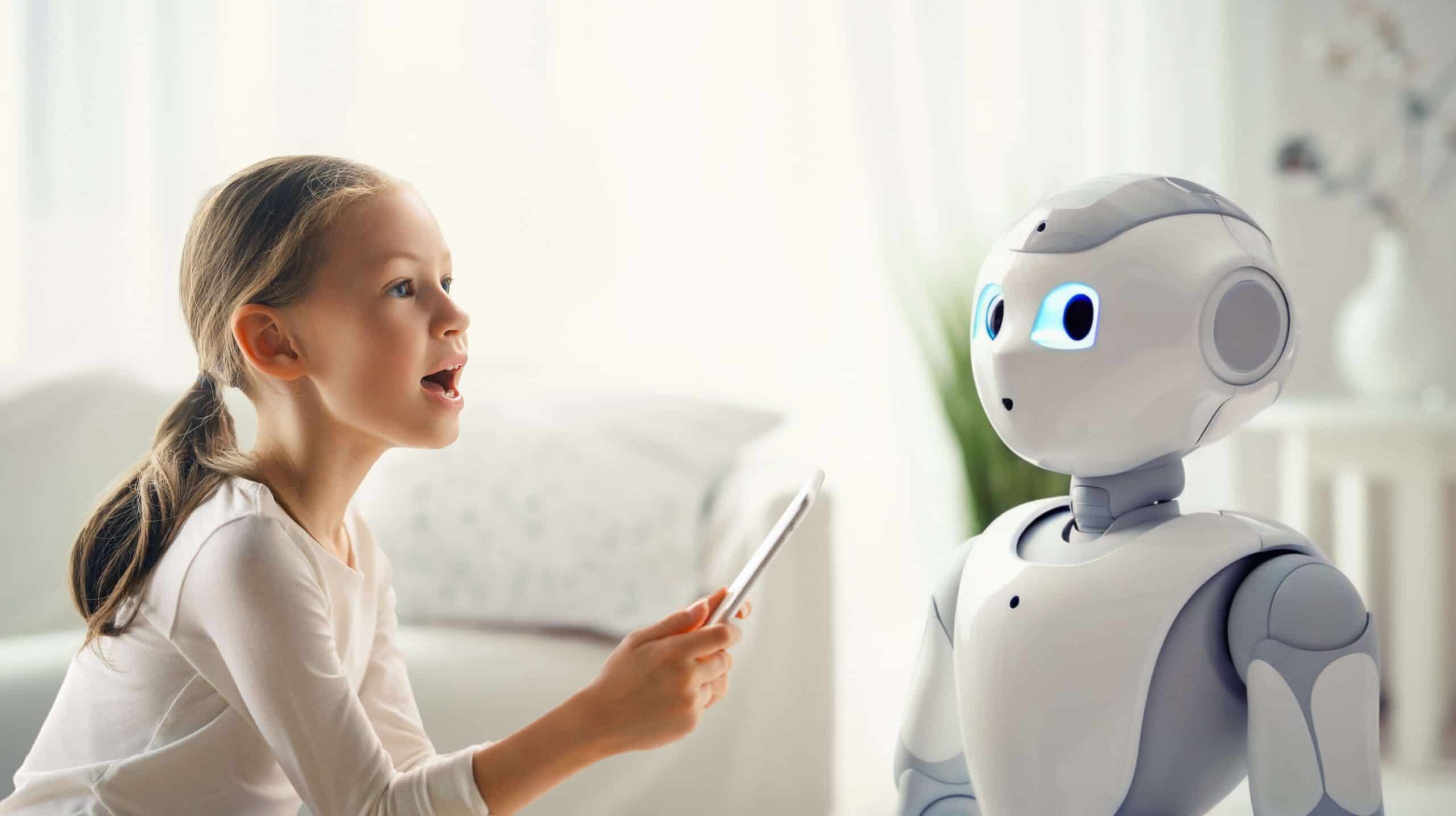
Human digital twins in education and training
Digital twins can also be very useful in education and training. Imagine a digital canvas mirroring not just objects but our learning selves. Organisations like the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) — a technical professional society dedicated to advancing tech and innovation — are at the forefront of these developments. Digital twins are the next frontier in education. They enable bespoke learning experiences — think of them as virtual clones that learn in tandem with us. Digital twins could become sophisticated personal tutors, reflecting not only our current knowledge but also the skills we’ve honed and those we let slip through the cracks of our busy lives. They could adapt our learning paths to address our weaknesses, recommend resources, and simulate real-world scenarios for hands-on experience.
Using advanced technologies such as the IoT, AI, and machine learning, digital twins can simulate real-time learning environments, allowing students to interact with virtual representations of what they study — be it a historical monument, a complex molecule, or a mathematical model. This offers a risk-free, immersive learning experience where trial and error are encouraged. Moreover, these digital twins have the potential to vastly improve training programmes. They could predict when we need a refresher course or suggest new topics to explore based on our digital footprint’s evolution. This could be particularly useful for professionals in fast-evolving fields, where staying updated is crucial. The idea also includes a system where both we and our digital twins learn from each other. Our digital twins will do more than just show what we’ve learned; they will also help shape the educational material we see, making it fit our changing interests and what we need to learn next. This is a lively, two-way process that goes beyond old-school learning. This digital version of our learning selves could become a key part of personalised learning, changing not just based on what we know, but also on how we learn best.
The Digital Society School’s project on practical education offers a compelling illustration of digital twin technology in education. This initiative explored the use of digital twins for students and teachers, the entire campus, and the courses offered. The idea behind this was to make learning more hands-on by providing a sense of location, physical presence, and connection — elements that are usually missing in online interactions. Key experiments within this project included the creation of student avatars and the development of a hybrid campus. The avatar concept allowed students to explore professional roles and personal identities through augmented reality applications and platforms like Gather and Mibo, enhancing online presence and interaction. The hybrid campus blends physical and digital learning spaces with virtual reality, creating engaging and inclusive experiences for both remote and on-site students. This strategy showcases the power of digital twins in developing immersive educational environments that meet the diverse needs of students, enhancing the learning journey for everyone.
Now you can transcend the limitations of the physical world and leave a lasting legacy by preserving your unique appearance, thoughts, experiences, and memories through a simple three-step clone creation process.
Create a virtual clone of yourself and live forever — digitally
What if there was a world where you could create a digital clone of yourself and live forever, not in a physical form, but in the realm of artificial intelligence? This groundbreaking concept is now a reality thanks to eternity.ac, an innovative startup that is paving the way to immortality. Eternity.ac enables you to transcend the limitations of the physical world and leave a lasting legacy by preserving your unique appearance, thoughts, experiences, and memories through a simple clone creation process.
The possibilities that arise from this technology are awe-inspiring. Imagine being able to interact with your loved ones even after they are no longer with us. Fans and followers could have meaningful interactions with their favourite public figures, and we could gain a deeper understanding of different viewpoints and experiences. The clone is designed to be incredibly lifelike, so you can engage in written chats or oral conversations with your digital self. It is also available in multiple languages, including English, Spanish, Portuguese, Polish, Ukrainian, and Belarusian.
Creating your digital clone on eternity.ac is very easy. First, you record your thoughts by answering a series of questions, sharing your wisdom, experiences, and memories. Next, you upload a few selfies from different angles, which are used to construct a lifelike 3D avatar of yourself. Finally, your personal clone is saved to the cloud, and you can share it with others using a link. If you prefer to keep your clone safe and secure, you can download it to a local storage device or even purchase an encrypted USB flash drive specifically designed for your clone, ensuring that your digital self will endure for eternity. The concept of digital cloning opens up a world of possibilities, where we can transcend the limitations of time and physical existence. It allows us to leave a lasting legacy, connect with others on a deeper level, and explore the untapped potential of artificial intelligence.
“Over the coming year, we will witness a rise of evil digital twins. This malicious virtual software model will be used to enhance cybercriminal activities such as ransomware, phishing, and highly targeted cyber warfare. Such attacks will demonstrate a significant increase in effectiveness compared to traditional methods”.
Jason M. Pittman, cybersecurity expert
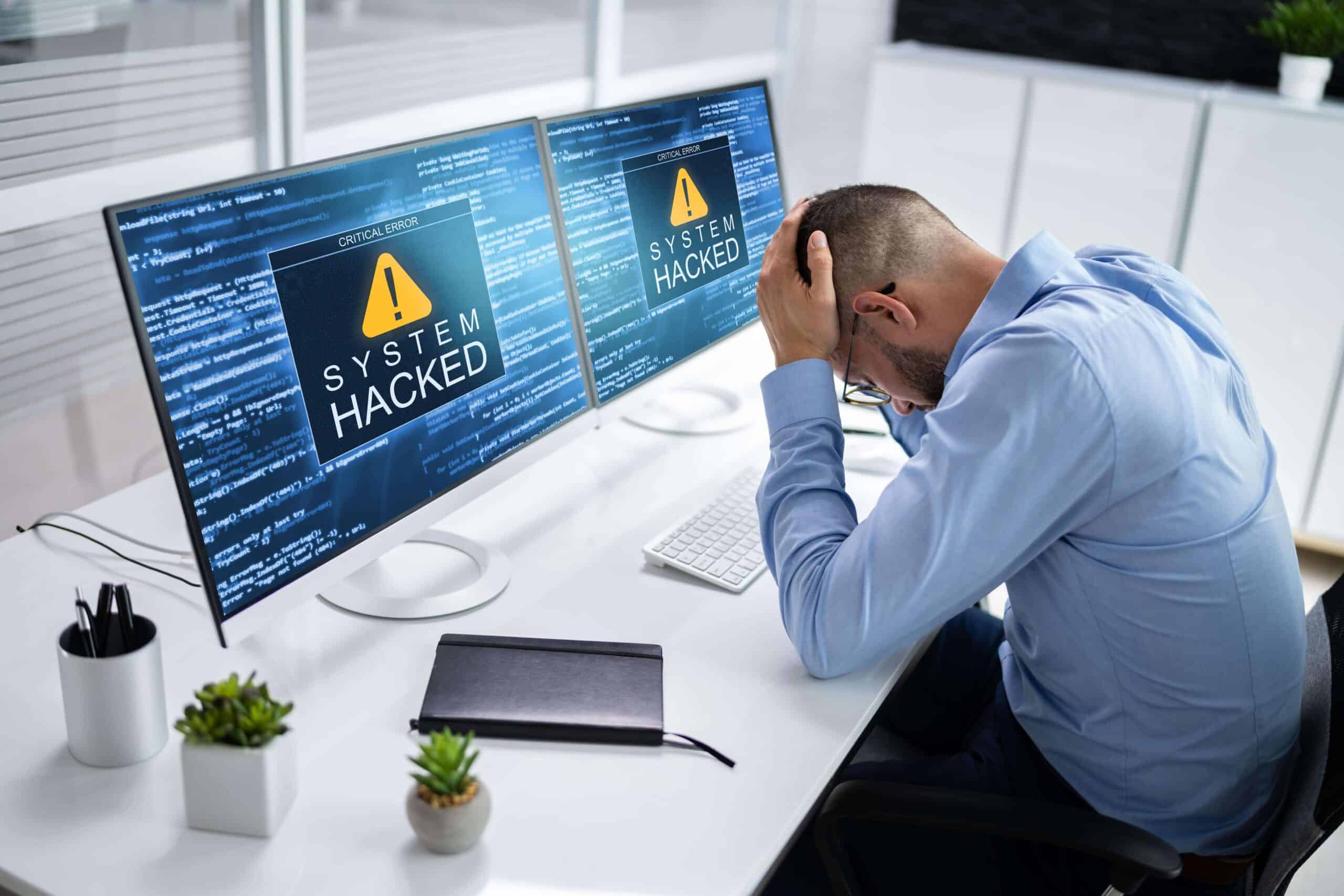
Beware the evil digital twin
Digital twins offer numerous benefits and applications across various industries, but they also introduce a set of potential downsides and security risks that need to be addressed. One of the primary concerns is that digital twins can be as vulnerable to cyber threats as traditional IT and operational technology environments. They can become entry points for attacks and even give rise to new forms of malicious activities, such as the ‘evil digital twin’. Technology and security experts emphasise the need for comprehensive security measures when creating digital twins. This includes securing all endpoints, the cloud platform where the twin operates, and the data being fed into the system. The interconnected nature of digital twins expands the attack surface that hackers can exploit, making them potential targets for cybersecurity breaches.
Jason M. Pittman, an expert in cybersecurity, warns about the rise of malicious virtual software models designed to enhance cybercriminal activities. He explains: “Over the coming year, we will witness a rise of evil digital twins. This malicious virtual software model will be used to enhance cybercriminal activities such as ransomware, phishing, and highly targeted cyber warfare. Such attacks will demonstrate a significant increase in effectiveness compared to traditional methods because of the specificity provided through the evil digital twin models”. He continues: “A hacker could create a digital twin of an existing persona, insert it into your environment and then watch and participate in your organisation and then inject malware into the ecosystem. This gives hackers another avenue in, and it’s unlikely there’s a defence for this”. Organisations should stay vigilant and up-to-date with the evolving threat landscape to proactively address emerging risks. While digital twins offer immense potential, it is essential to acknowledge and address the downsides and security concerns associated with their adoption. By implementing a proactive and comprehensive approach to security, organisations can maximise the benefits of digital twins while minimising the risks they pose.
In closing
To say we’re exploring new ground with digital twins and their use in healthcare and education would be an understatement. But with these exciting possibilities, we also face significant challenges. How will we handle the privacy concerns, ethical issues, and the risk of misuse that come with digital twins? The idea of these virtual human clones improving our health and education, and keeping our memories alive for future generations is fascinating. However, we must also be wary of the risks, such as the creation of harmful digital twins used for cybercrimes, which highlight the need for strong security and ethical standards.
As digital twins become more common, driven by advancements in technology, it’s important for everyone — developers, ethicists, policymakers, and the public — to work together to guide their development in a way that matches our shared values and goals. When thinking about the role of digital twins in our future, we must balance the excitement of innovation with careful consideration of its impact. How will we ensure that digital twins make our lives better without compromising our privacy or security? Answering these questions will determine how digital twins will affect our lives and society, aiming to improve our wellbeing while staying true to ethical principles.